Many efficacious drugs have limited therapeutic potential because of toxicity, while other drugs may have efficacy limitations due to biodistribution, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics. Our proprietary AIDE technology uses an automated process designed to encapsulate a drug into the patient’s own red blood cells to deliver a therapy in a potentially more effective and safer method. Autologous red blood cells have several characteristics that make them an ideal vehicle for drug delivery:
Potential for improved biodistribution as encapsulated drug in autologous red blood cells is designed to enable the slow release of the drug from the red blood cells while circulating through various tissue beds.
Potential for altered pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, including long circulating half-life, and altered or improved tissue biodistribution. The altered pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the encapsulated drug may significantly increase the desired therapeutic effect and improve the safety profile of the therapy.
Potential for the encapsulation of small or large molecules, peptides, and proteins inside of autologous red blood cells to limit biodegradability and immunogenicity..
Potential for avoiding issues with donor compatibility associated with heterologous cells.
eDSP (previously referred to as EryDex) is the first product in development that leverages our AIDE technology and is composed of dexamethasone sodium phosphate (DSP) encapsulated in autologous red blood cells targeted for the treatment of patients with Ataxia-Telangiectasia, or A-T. DSP is a corticosteroid well described for its anti-inflammatory properties, but is coupled with serious adverse effects, including potential long-term adverse effects due to adrenal suppression. eDSP is designed to maintain the efficacy of corticosteroids while reducing or eliminating the significant adverse effects associated with corticosteroid treatment. Our AIDE technology is designed to encapsulate DSP in a patient’s own red blood cells and to alter the biodistribution, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of the DSP to deliver a therapy in a potentially more effective and safer method.
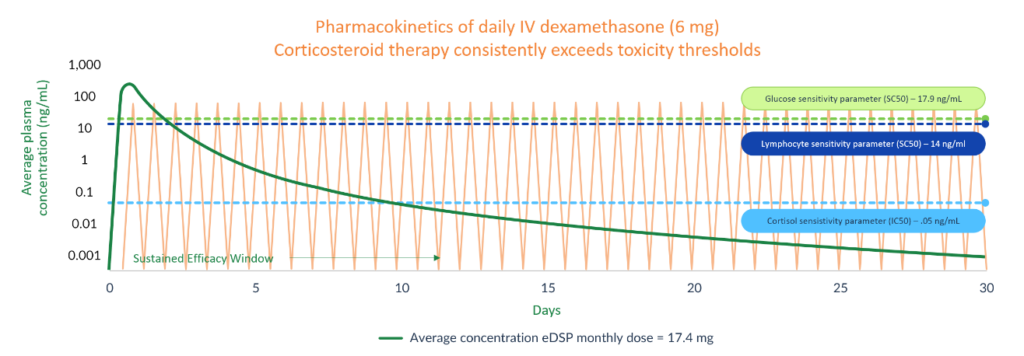
The optimal efficacy of corticosteroids is the result of two pharmacokinetic characteristics: 1) an initial bolus to achieve a high Cmax that results in high levels of corticosteroid receptor occupation; and 2) sufficient sustained tissue concentrations that allow for continued receptor site occupancy over time.
In order for a conventional corticosteroid to achieve these characteristics, the drug must be dosed frequently, typically daily. Long-term daily dosing regimens sufficient to provide efficacy, lead to chronic adverse effects such as hyperglycemia, immunosuppression, and suppression of the HPA axis. Corticosteroid therapy without significant long-term safety liabilities would represent a major advancement in the treatment of many chronic diseases where corticosteroids are already known to be beneficial.
Note: Pharmacokinetic (PK) curve from Population PK model (smoothed) based on company’s prior studies of eDSP. Information represented does not reflect a completed comparative study of eDSP versus oral/IV administration of dexamethasone, but rather provides a comparison of published corticosteroid pharmacokinetic information relative to company data regarding eDSP. IC50 and SC50 refer to pharmacodynamic parameters of which IC50 reflects drug concentration eliciting 50% of the maximum inhibition and SC50 reflects drug concentration eliciting 50% of the maximum stimulation. References: Montanha et al, Frontiers in Pharmacology (2022) 13: 814134; Krzyzanski et al, Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics (2021) 48: 411-438; Świerczek A, Jusko WJ., Clinical and Translational Science (2023) 16(9):1667-1679.
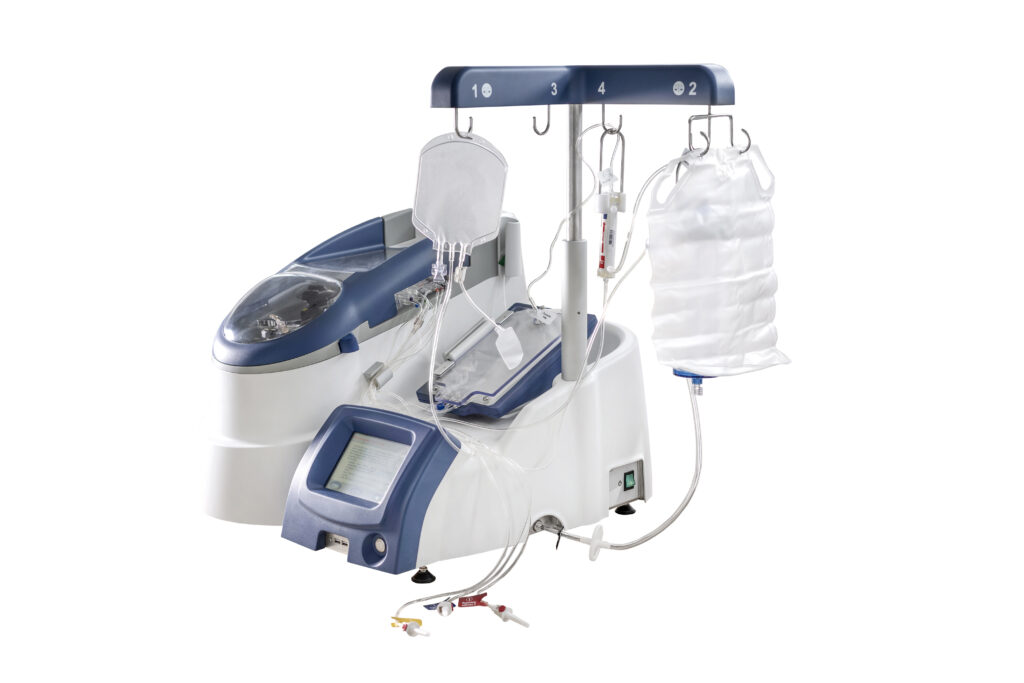
Our proprietary AIDE technology platform is a novel drug/device combination that uses an automated process designed to encapsulate a drug into the patient’s own red blood cells. The AIDE technology drug/device combination consists of a specialized automated equipment including the RCL and a sterile single-use treatment kit.
The automated AIDE process and treatment is designed to be completed at the point-of-care and includes a series of steps which take approximately two hours from start to finish.